Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common concern for diabetic individuals, impacting their quality of life. Viagra, a well-known medication for ED, raises questions regarding its safe and effective use among diabetics. Understanding the appropriate dosage is crucial to managing both conditions effectively.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetics
Diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes, significantly increases the risk of developing erectile dysfunction. This occurs due to the damage diabetes can cause to blood vessels and nerves, crucial for achieving and maintaining an erection. The prevalence of ED in diabetic men is notably higher compared to the general population, making it a pertinent issue in diabetes management.
Viagra and Its Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, belongs to a class of drugs known as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. It works by enhancing blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation, aiding in achieving and sustaining an erection. This mechanism is beneficial for diabetic individuals experiencing ED, as it addresses the physiological barriers caused by diabetes.
Factors Affecting Viagra Dosage for Diabetics
- Severity of Erectile Dysfunction: The extent of ED symptoms varies among diabetic men. A higher severity may necessitate a different dosage compared to mild cases.
- Diabetes Management: Well-controlled diabetes may affect how Viagra interacts with the body. Poorly managed diabetes can complicate the effectiveness of the medication.
- Other Health Conditions: Concurrent health issues such as cardiovascular diseases or kidney problems can influence the dosage prescribed.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines
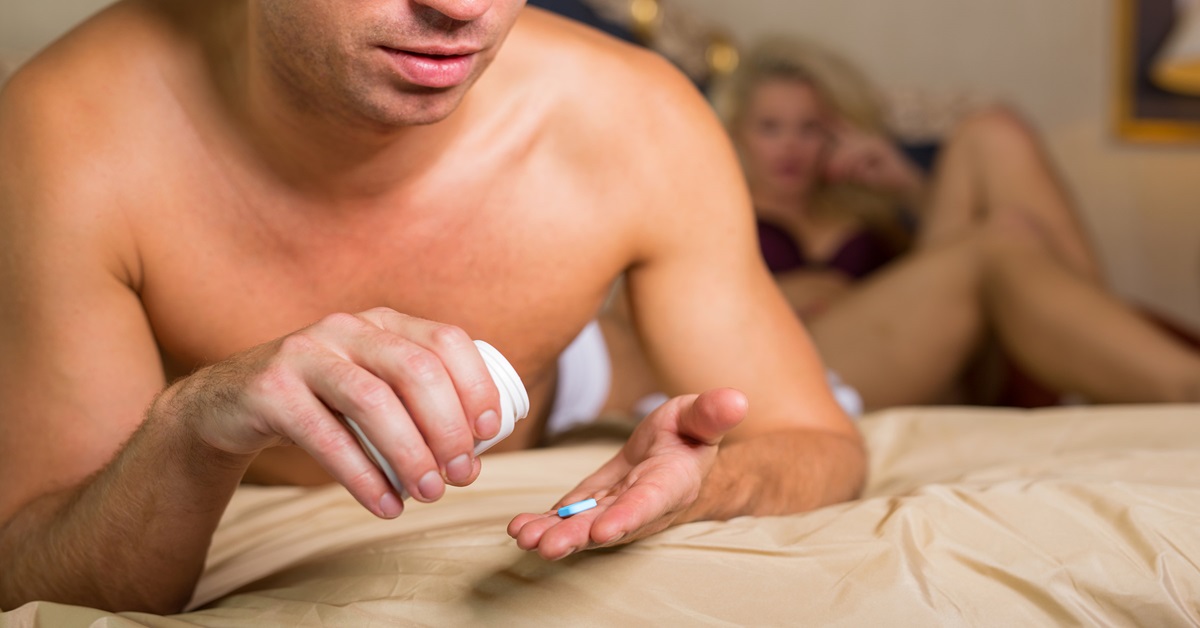
The standard starting dose of Viagra for most adults without specific health considerations is 50 milligrams (mg) taken as needed, approximately one hour before sexual activity. However, for diabetic individuals, especially those with underlying health concerns, dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Tailoring Dosage for Diabetic Patients
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Diabetic patients should consult their healthcare provider for personalized advice. Factors such as age, overall health, and severity of ED and diabetes are considered when determining the appropriate dosage.
- Initial Dosage Adjustment: Starting with a lower dose, such as 25 mg, is often recommended for diabetic individuals. This helps gauge the body’s response to the medication while minimizing potential side effects.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular monitoring is essential to assess the effectiveness and safety of the chosen dosage. Healthcare providers may adjust the dosage based on individual response and tolerability.
Potential Risks and Considerations
- Hypoglycemia Risk: Viagra can lower blood pressure, which may interact with diabetes medications. Close monitoring is necessary to prevent hypoglycemia episodes.
- Interaction with Diabetes Medications: Certain diabetes medications and Viagra may interact unfavorably. It’s crucial to inform healthcare providers of all medications being taken.
- Cardiovascular Health: Diabetic individuals often have underlying cardiovascular issues. Viagra’s effects on blood pressure should be carefully considered to avoid complications.
Conclusion
Determining the appropriate dosage of Viagra for diabetic individuals requires careful consideration of various factors. Consulting healthcare providers ensures personalized care that considers the unique needs and health status of each patient. By managing both diabetes and erectile dysfunction effectively, individuals can improve their overall quality of life and sexual health.
In conclusion, while Viagra is a viable option for treating ED in diabetic patients, its dosage should be tailored to individual health needs. Proper consultation with healthcare providers remains essential in achieving optimal outcomes.